Physics Formula electric charges and fields
Physics Formula – 1
Apply Coulomb’s law
q1 = first charge
q2 = Second charge
r = distance between both charge
ε0= permittivity of free space
1/4πε0 = 9 x 109 Nm2C-2
 |
| Coulomb’s law |
Coulomb’s force law between two point charges q1 and q2 located at r1 and r2 is then expressed as
 |
| Coulomb’s force law between two point charges |
Physics Formula – 3
Thus the total force F1 on q1 due to the two charges q2 and q3 is given as
| total force F1 on q1 due to the two charges q2 and q3 |
Physics Formula – 4
Coulomb’s law of resultant force
 |
| Coulomb’s law of resultant force |
Physics Formula – 5
The electric field produced by the charge Q at a point r is given as
 |
| electric field produced by the charge Q at a point r |
Physics Formula – 6
Vactor Force F exerted by a charge Q on a charge q
 |
| Vactor Force F exerted by a charge Q on a charge q |
Physics Formula – 7
The electric field E at r due to the system of charges is
 |
| electric field E at r due to the system of charges |
Physics Formula – 8
The total flux φ through a surface S is
φ ≈ Σ E.ΔS
Physics Formula – 9
the electric field of a dipole at large distances takes simple forms:
At a point on the dipole axis
 |
| electric field of a dipole at a point on the dipole axis |
At a point on the equatorial plane
 |
| electric field of a dipole a point on the equatorial plane |
Physics Formula – 10
Surface charge density σ at the area element by
 |
| Surface charge density σ at the area element |
Physics Formula – 11
The linear charge density of a wire is defined by
 |
| linear charge density of a wire |
Physics Formula – 12
The volume charge density (sometimes simply called charge density) is defined as
 |
| volume charge density |
Physics Formula – 13
Electric field due to the charge ρΔV is given by Coulomb’s law:
 |
| Electric field due to the charge ρΔV is given by Coulomb’s law |
Physics Formula – 14
The total electric field due to the charge distribution is obtained by summing over electric fields due to different volume elements:
 |
| total electric field due to the charge distribution |
Physics Formula – 15
Total flux through a sphere of radius r, which encloses a point charge q at its centre.
 |
| Total flux through a sphere of radius r |
Physics Formula – 16
Electric flux through a closed surface S
∆ φ1 = q/ε0
Physics Formula – 17
Flux through the Gaussian surface
 |
| Flux through the Gaussian surface |
Physics Formula – 18
Field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet
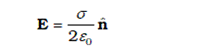 |
| Field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet |
n is a unit vector normal to the plane and going away from it
Physics Formula – 19
Field outside the shell
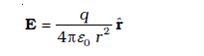 |
| Field outside the shell |
Field inside the shell
E=0
No comments:
Post a Comment