CARBON COMPOUND
Carbon is an element. The symbol of carbon is C. It is a non-metal. The name carbon is derived from the Latin word 'carbo' which means 'coal'. The amount of carbon present in the earth's crust and atmosphere is very small. the earth's crust contains only 0.02% carbon and the atmosphere has only 0.03% of carbon dioxide gas. all the living things, plants and animals, are made up of carbon based compounds which are called organic compounds. Thus, carbon element is present in all living things.
Occurrence of Carbon
Carbon occurs in nature in 'free state' (as element) as well as in the 'combined state'
In free state,carbon occurs in nature mainly in two forms: diamond and graphite.
In the combined state, carbon occurs in nature in the form of compounds such as :
(i) Carbon dioxide gas in air
(ii) Carbonates (like limestone, marble and chalk)
(iii) Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas
The various physical forms in which an element can exist are called allotropes of the element.
Three allotropes of carbon are
1. Diamond
· Diamond is a colourless transparent substance having extraordinary brilliance (chamak)
· It is the known hardest natural substance.
Reason : The rigid structure of diamond makes it a very hard substance.
· Diamond does not conduct electricity.
Reason:there are 'no free electrons' in a diamond crystal, it does not conduct electricity.
· The melting point of diamond is also very high, being more than 3500°C.
Reason : This is because a lot of heat energy is required to break the network of strong covalent bonds in the diamond crystal.
· If we burn diamond in oxygen, then only carbon dioxide gas is formed and nothing is left behind. This shows that diamond is made up of carbon only.
How identify : The carbon dioxide formed by burning graphite can turn lime water milky.
· The carbon dioxide formed by burning diamond
Uses of Diamond
· Diamonds are used in cutting instruments like glass cutters
· Diamonds are used for making jewellery
· Sharp-edged diamonds are used by eye-surgeons as a tool to remove cataract from eyes
 |
| Diamond structure |
2. Graphite
· Graphite is a greyish-black opaque substance
· Graphite is lighter than diamond.
· Graphite is soft and slippery to touch.
Reason :the various layers of carbon atoms in graphite are joined by weak forces, they can slide over one another.· Graphite conducts electricity.
Reason : Due to the 'presence of free electrons' in a graphite
· The carbon dioxide formed by burning graphite
· If we burn graphite in oxygen, then only carbon dioxide gas is formed and nothing is left behind. This shows that graphite is made up of carbon only.
· The carbon dioxide formed by burning graphite
Uses of Graphite
· powdered graphite is used as a lubricant for the fast moving parts of machinery.
· graphite is used for making carbon electrodes or graphite electrodes in dry cells and electric arcs.
· Graphite is used for making the cores of our pencils called 'pencil leads' and black paints
 |
| Graphite structure |
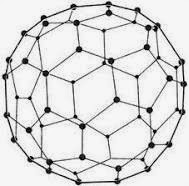
1. Buckminsterfullerene
· Buckminsterfullerene is an allotrope of carbon containing clusters of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules.
· There are twenty hexagons and twelve pentagons of carbon atoms in one molecule of buckminsterfullerene.
· Buckminsterfullerene is a dark solid at room temperature.
· If we burn buckminsterfullerene in oxygen, then only carbon dioxide gas is formed and nothing is left behind. This shows that buckminsterfullerene is made up of carbon only.
 |
| Buckminsterfullerene structure |
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
· The compounds of carbon are known as organic compounds.
· Organic compounds are covalent compounds having low melting points and boiling points. Most of the carbon Compounds are non-conductors of electricity. Organic compounds occur in all living things like plants and animals.
· Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, carbonates, hydrogen carbonates and carbides are also carbon compounds but They are not considered to be organic compounds.
Reason : This is because their properties are very different from those of the common organic compounds.
· The study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry.
· There are more than 5 million organic compound.
Catenation (self-linking)(Figure) : carbon atoms can link with one another by means of covalent bonds to form long chains (or rings) of carbon atoms. This property of carbon compound is known as catenation or self linking. This property of carbon compound is responsible for existence of a large number of organic compounds.
Tetravalency (four valency) : Valency of carbon element is 4 which is quite large and responsible for existence of a large number of organic compounds
HYDROCARBONS
A compound made up of hydrogen and carbon only is called hydrocarbon (Hydrogen + Carbon = Hydrocarbon). The most important natural source of hydrocarbons is petroleum (or crude oil)
Types of Hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are of two types :
1. Saturated hydrocarbons and 2. Unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Saturated Hydrocarbons (Alkanes):
· A hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected by only single bonds is called a saturated hydrocarbon.
· An alkane is a hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected by only single covalent bonds (There are no double or triple bonds in an alkane). -C-C-
· The general formula of saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes is CnH2n +2 where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule of the alkane.
· Put n = 1,2,3… we get
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons (Alkenes and Alkynes)
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are of two types :
(i) alkenes and (ii) alkynes.
(i)Alkenes
· An unsaturated hydrocarbon in which the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond is called an alkene. 

· The general formula of an alkene is CnH2n where n is the number of carbon atoms in its one molecule.
· The Value of n can not one because alkene compound need at least two carbon atom to form double bond between C to C
· Examples
(ii) Alkynes :
· An unsaturated hydrocarbon in which the two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond is called an alkyne.
· The general formula of alkynes is CnH2n where n is the number of carbon atoms in one molecule of the alkyne.
· When n = 2 we get C2H 2 which is known as acetylene or ethyne.
Examples
Alkyl Groups
· The group formed by the removal of one hydrogen atom from an alkane molecule is called an alkyl group.
· The general formula of an alkyl group is CnH2n +1where n is the number of carbon atoms
· Examples of alkyl group are methyl group (CH3-) and ethyl group (C2H5- ).
Cyclic compound :
Saturated cyclic compound
Cyclohexane C6H12
Electron-dot structure of cyclohexane has been obtained by putting two electron dots in place of every single bond in its structural
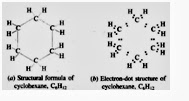 |
| Cyclohexane C6H12 |
The molecular formula of cyclopentane is C5H10. Cyclopentane has 5 carbon atoms in the form of
a pentagonal ring which are connected by single bonds.
Benzene is C6H6
Electron-dot structure of benzene has been obtained by putting two electron dots in place of every single bond and four electron dots in place of every double bond in its structural formula.
 |
| Benzene C6H6 |
Isomers
The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers.
Isomerism is possible only with hydrocarbons having 4 or more carbon atoms
no isomerism is possible in methane, ethane and propane because they contain only one, two or three carbon atoms respectively
Example n-butane and iso-butane
Compound Number of Isomers
butane (C4H10) 2
pentane (C5H12) 3
hexane (C6H14) 5




